 Hello, readers welcome to new post. Today we will discuss Difference between %d and %i format specifiers in C language. In C language of programming %d and %i are called format specifiers. %d was used to specify the variable type as decimal and %i used for integer specification.
Hello, readers welcome to new post. Today we will discuss Difference between %d and %i format specifiers in C language. In C language of programming %d and %i are called format specifiers. %d was used to specify the variable type as decimal and %i used for integer specification.
Note: %d is used to specify signed decimal integers and %i specifies integer
Simply, there is no difference for print() function output but printing in numbers through the use of %d or %i but for the use of scanf function differences exist. scanf() can detect base through %i but suppose base ten for %d. In this tutorial, we will learn some points that will help us to find the basic difference between %d and %i. So let’s get started
What is Format specifiers in C
- The format specifier are used in C programming language to define the input and outputs. Formate specifiers help the compiler to know the type of data in a variable when get input through use of scanf() function and printing using print() function
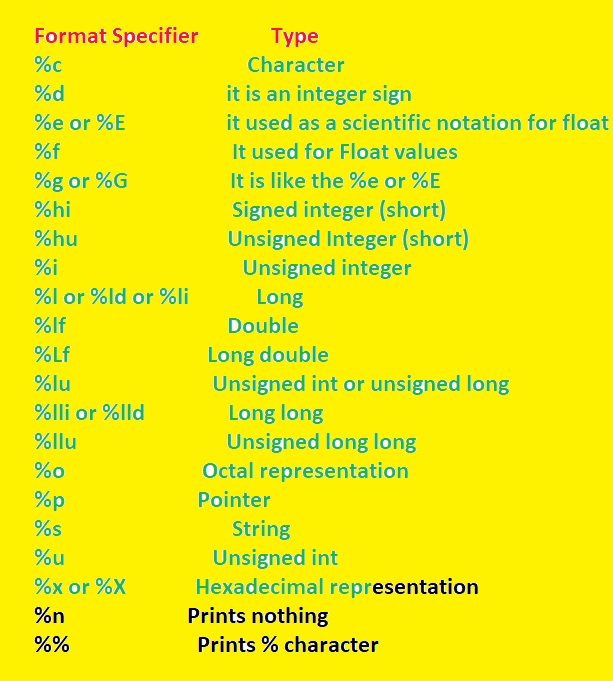
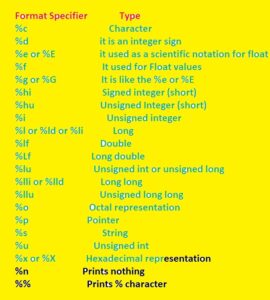
- Commonly used Format specifiers are listed here
Format Specifier | Type |
| %c | Character |
| %d | it is an integer sign |
| %e or %E | it used as a scientific notation for float |
| %f | It used for Float values |
| %g or %G | It is like the %e or %E |
| %hi | Signed integer (short) |
| %hu | Unsigned Integer (short) |
| %i | Unsigned integer |
| %l or %ld or %li | Long |
| %lf | Double |
| %Lf | Long double |
| %lu | Unsigned int or unsigned long |
| %lli or %lld | Long long |
| %llu | Unsigned long long |
| %o | Octal representation |
| %p | Pointer |
| %s | String |
| %u | Unsigned int |
| %x or %X | Hexadecimal representation |
| %n | Prints nothing |
| %% | Prints % character |
%d vs %i format specifier in C language
- We will get the difference according to printf and scanf. First for printf
- For printf, there is no difference between %i and %d format specifier. Let’s solve an example
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num = 15;
// print value for %d
printf(“num ans for %%d is = %d\n”, num);
// print value using %i
printf(“num ans for %%i is = %i\n”, num);
return 0;
}
Output:
num ans for %d is = 15
num ans for %i is = 15
Now find the difference on the basis of scanf
- In the case of scanf function %d suppose the base as 10 but %i detects the base. So these two specifiers work in different fashions during input specifier configuration. So in simple form 015 will be 10 for %d and 15 for %i
- Solve example
include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=0;
int b=0;
printf("Put value a: ");
scanf("%d",&x);
printf("Put value b: ");
scanf("%i",&b);
printf("a=%d, b=%d\n",a,b);
return 0;
}
put value of a:20
put vaue of a:0x30
a=20, b=30
That is all about the Difference between %d and %i format specifiers in C language all details has explained.If you have any questions ask them here.
Read also